0. Abstract
생략
1. Introduction
- 2D human pose estimation은 중요한 문제이지만, 그러나 computer vision영역에서는 challenging problem이였다.
- 본 논문은 single-person pose estimation에 관심을 두고 있다. ( 이는 나중에 multi-person pose estimation의 기초가 된다!)
- 대부분 존재하는 기법들은, 직렬(series)로 연결된 high-to-low resolution subnetworks를 통과하고, 그리고 해상도를 복구하는 방법을 이용한다.(ex. Figure2 - (a)Hourglass: 대칭적인 구조를 이용 ,(c) SimpleBaseline: transposed convolution layers를 이용하여 highresolution으로 복구, )
- 예를들어, Hourglass의 경우는 대칭적인 구조를 사용하여 저해상도 이미지를 고해상도로 복구하고, SimpleBaseline의 경우 transposed convolution layers를 이용하여 고해상도로 복구한다. 게다가, dilated convolution을 이용하여high-to-low resolution network의 마지막 layer를 blow-up한다. (ex. VGGNet, ResNet)
(FIgure2 (a) : Hourglass, (c) : SimpleBaseline, (d) : dilated convolution 이용 예시)

- 본 논문에서는 우리는 전체 과정에서 고해상도 표현(high-resolution representations)을 유지할 수 있는 High-Resolution Net(HRNet)이라는 새로운 architecture를 제시한다.
- 본 논문에서는 high-resolution subnetwork를 first stage로 시작하여 점차 high-resolution subnetwork를 하나씩 추가하여 더 많은 단계를 형성한다. 그리고 그렇게 생성된 multi-resolution subnetworks를 병렬(parallel)하게 연결한다.

- 본 논문에서는 해당 네트워크를 통과한 high-resolution representations를 이용하여 key-points를 추정한다고 한다.
- 본 논문에서 제시한 network는 기존의 포즈 추정을 위해 널리 쓰이는 networks에 비교하여 2 가지 이점이 있다.
1) 본 모델은 직렬이 아닌 병렬로 high-to-low resolution subnetworks을 연결하였기 때문에, 기존의 방법처럼 low-to-high 과정을 통해서 resolution을 복구하는 것이 아니기 때문에, 예상되는 heatmap은 potentially 더욱 정교하다.
(Q. 원래 그럼 그냥 high-resolution으로 적용하면 되는게 아닌가?)
2) 대부분 존재하는 융합 체계 (fusion scheme)은 low-level 과 high-level representations을 종합한다. (aggregate) 대신, 본 논문에서는 동일한 깊이와 유사한 수준에서 low-resolution representations의 도움을 받아 high-resolution representations를 활성화 하기 위해 반복적인 multi-scale fusion을 수행하며, 그 반대의 경우도 마찬가지이므로, high-resolution representations은 pose 추정에도 풍부하다.
--> 결과적으로, 본 논문에서 예측되는 heatmap은 잠재적으로 더욱 정확할 수 있게 된다.
2. Related Work
생략
3. Approach
- Human pose estimation,일명 keypoint detection은 크기가 W*H*3인 image I로부터 K개의 keypoints 혹은 부분들(e.g., elbow, wrist,..)의 위치를 탐지하는데 목적을 두고있다.
- 최근의 기법은, 이 문제를 크기 W*H, { H1, H2, ....., Hk}의 K heatmaps의 추정으로 변환한다.
- 본 논문에서는 널리 보급된 pipeline인(Fig2, (a), (b), (c))를 따라 human keypoints를 예측하기 하는데, 이는 해상도를 감소시키는 두 개의 strided convolutions, input feature maps와 같은 해상도인 feature maps를 결과로 내는 main body, 그리고 어떤 keypoint positions이 선택 되고 full resolution(전체 해상도)로 변환되는 heatmaps을 추정하는 regressor가 존재하는 줄기로 구성되어 있다. (Fig 1.)
* Sequential multi-resolution subnetworks
- pose estimation에 존재하는 networks은 high-to-low resolution subnetworks를 직렬로 연결하여 구축되며, 여기서 스테이지를 구성하는 각 하위 네트워크(subnetwork)는 일련의 convolutions으로 구성되며 인접한 subnetwork에 걸쳐 downsampling layer가 있어 해상도를 절반으로 낮춘다.

* parallel multi-resolution subnetworks
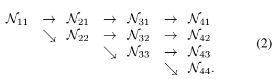
* Repeated multi-scale fusion
- 본 논문에서는 병렬의 subnetworks를 가로지르는 exchange units를 이용하여, 각 서브 네트워크는 반복적(reapeatedly)으로 다른 병렬 서브 네트워크로부터 정보를 수신한다.


* Exchange unite

- downsampling : 3*3 convolution, stride 2을 통해 진행하였다.
- upsampling : nearest neighbor sampling following a 1*1 convolution for aligning the number of channels
* Heatmap estimation
- 실험적으로 마지막 exhange unit 후의 high-representations output으로부터 heatmap을 역행하였다. l
- loss function은 mean squeared error를 이용하였는데, 이는 groundtruth heatmap과 predicted heatmaps을 비교할때 적용되었다.
- ground truth heatmaps은 grouptruth(진짜 이렇게 적혀있음 근데 뭔지 모르겠음..) 위치를 중심으로 표준 편차가 1pixel인 2D Gaussian을 적용하여 생성된다.
* Network instantiation
- HRNet, contains four stages with four parallel subnetworks, whose resolution is gradually decreased to a half, and accordingly, the width (the number of channels) is increased to double.
4. Experiments
4.1 COCO Keypoint Detection
Dataset.
- train : COCO train2017 dataset, including 57K images and 150 person instances
- evaluate : val2017 set and test-dev2017 set, containing 5000 images and 20K images, respectively
Evaluation metric.
- object Keypoint Similarity (OKS)

- AP50 ( AP at OKS = 0.50)
- AP75,
- AP ( the mean of AP scores at 10 positions, OKS = 0.50, 0.55, .....0.90, 0.95)
- AP(M) : for medium objects
- AP(L) : for large objects
- AR at OKS = 0.50,0.55,...,0.90,0.955
Training
- width : height = 4:3 ( human detection box)
- size : crop the box from the image, which is resized to a fixed size,256*192, 384*288
- augmentation : random rotation([-45,45]), random scale, flipping
* half-body data augmentation is al involved
Test
- two stage
1) detect the person instance using a person detector : provided by Simple-Baseline
2) predict detection keypoints




